Diabetes Care
-
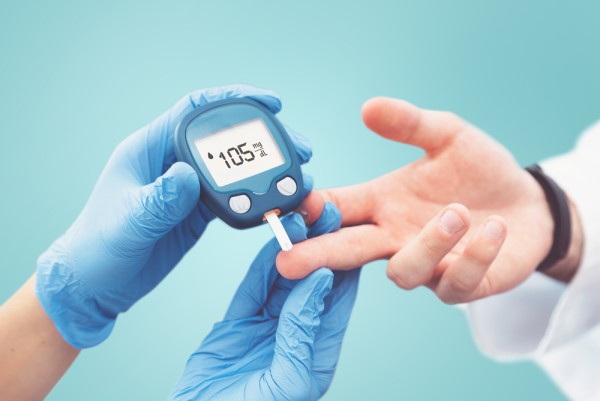
Blood sugar monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes. This can be done using a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system.
-
Medication management: Many people with diabetes require medication to help control their blood sugar levels. This may include insulin injections, oral medications, or other injectable medications.
-
Healthy eating: A balanced diet is crucial for managing diabetes. This typically involves monitoring carbohydrate intake, eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, and limiting foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats.
-
Regular exercise: Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. It's important for people with diabetes to engage in regular exercise, as recommended by their healthcare provider.
-
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing diabetes. For those who are overweight or obese, weight loss can improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications.
-
Education and support: Diabetes education programs can help individuals learn about their condition, develop self-care skills, and make lifestyle changes to better manage their diabetes. Support groups and counseling can also provide emotional support and motivation.
-
Monitoring and prevention of complications: Diabetes can lead to various complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help detect and prevent these complications.
-
Collaborative care: Diabetes care often involves a team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, dietitians, and diabetes educators. Collaborative care ensures that individuals receive comprehensive and personalized treatment.